Lexical Ambiguity
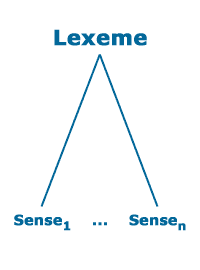
Lexical ambiguity occurs at the level of the lexical items of a language: the same phonetic or written word-form represents items of different syntactic categories with different meanings, or a lexical item of a certain category has multiple senses.
Here is an example where the lexeme BOOK has two senses:

Traditionally, two types of lexical ambiguity are distinguished:
